Image Wikipedia
The answers to the four questions posted earlier are in bold below.
- Switzerland—The period of the thirteen cantons in Swiss history, from 1513 to 1798, involved the Old Swiss Confederacy, a loose union of thirteen sovereign cantons united for mutual defence and foreign policy. These cantons were diverse in religion and culture, with some Catholic and others Protestant post-Reformation. The confederacy expanded in the 16th century due to its mercenary strength, gaining autonomy from the Holy Roman Empire while maintaining cantonal independence through treaties. Internal conflicts like the Wars of Kappel highlighted religious divisions, yet peace and neutrality prevailed. The era ended with the French invasion in 1798, leading to the Helvetic Republic and centralised governance.
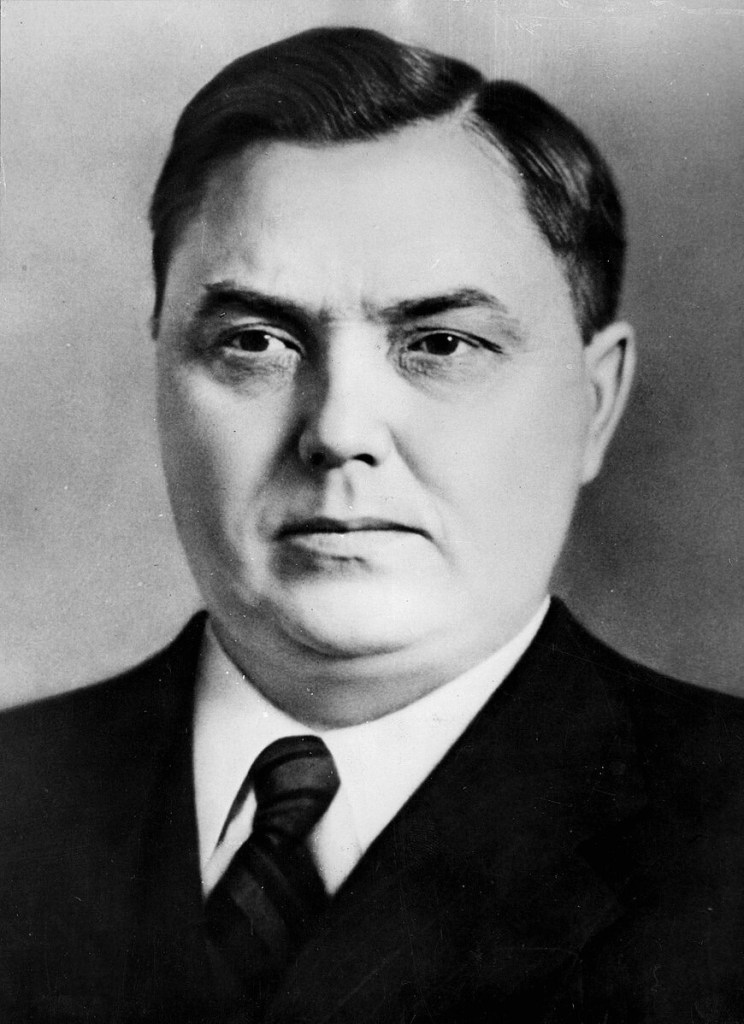

Georgy Malenkov
Image Wikipedia - Georgy Maximilianovich Malenkov—Georgy Malenkov served as the Premier of the Soviet Union from 1953 to 1955, succeeding Joseph Stalin. He aimed to improve the economy by focusing on consumer goods and agriculture, but faced opposition within the Communist Party. Malenkov also sought to decentralise the administration and reduce secret police power, but his reforms were resisted. In 1955, he resigned after a power struggle with Nikita Khrushchev, being replaced by Nikolai Bulganin. His tenure marked a brief shift towards economic reforms and a more open political atmosphere, which was reversed after his departure.
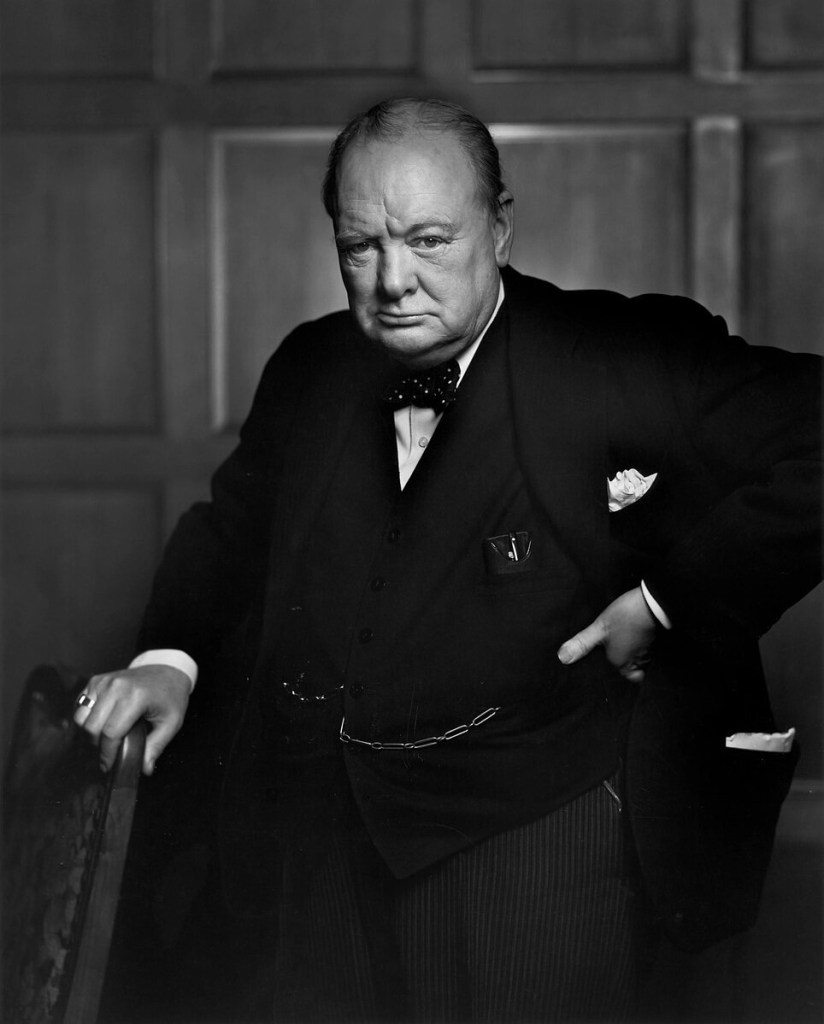

Winston Churchill, 1941
Image Wikipedia - Winston Churchill—Churchill’s Iron Curtain speech, delivered on March 5, 1946, at Westminster College, Fulton, Missouri, highlighted the need for the US and Britain to counter Soviet communism, which had created a political and ideological barrier across Europe. The term “iron curtain” described the USSR’s post-World War II isolation of eastern and central Europe from the West. Post-war, Western leaders were divided on how to engage with the Soviet Union, with some fearing Stalin’s expansionism and others believing in potential peace. Churchill and American diplomat George Kennan advocated for a containment policy, opposing Soviet expansion and advocating for Western military counterpressure. The relevant paragraph from his speech reads…
“From Stettin in the Baltic to Trieste in the Adriatic an iron curtain has descended across the Continent. Behind that line lie all the capitals of the ancient states of Central and Eastern Europe. Warsaw, Berlin, Prague, Vienna, Budapest, Belgrade, Bucharest and Sofia, all these famous cities and the populations around them lie in what I must call the Soviet sphere, and all are subject in one form or another, not only to Soviet influence but to a very high and, in some cases, increasing measure of control from Moscow.”
(The National Archives, full text.)
Heartbreak Hotel.
Image Wikipedia - Heartbreak Hotel—Heartbreak Hotel by Elvis Presley, released on January 27, 1956, was his first single with RCA Victor. Written by Mae Boren Axton, Tommy Durden, and Presley, it was inspired by a newspaper article about a man’s suicide. Recorded on January 10, 1956, with the Blue Moon Boys, Chet Atkins, and Floyd Cramer, it features an eight-bar blues progression and heavy reverberation. The song topped multiple charts, became Presley’s first million-seller, and was certified double platinum. It was inducted into the Grammy Hall of Fame in 1995 and named one of Rolling Stone’s 500 Greatest Songs of All Time in 2004.
